Multiple
Choice
Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the
question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Write a balanced half-reaction
for the reduction of permanganate ion, MnO4-, to MnO2 in a basic
solution. a. | MnO4-(aq) + 4 OH-(aq) + 3
e- → MnO2(s) + 2
H2O(l) + 2
O2(g) | b. | MnO4-(aq) + 2
OH-(aq) + 3 e- →
MnO2(s) + 2 HO2(aq) | c. | MnO4-(aq) + 3
e- → MnO2(s) +
O2(g) | d. | MnO4-(aq) + 2
H+(aq) + 3 e- →
MnO2(s) + 2 OH-(aq) | e. | MnO4-(aq) + 2
H2O(l) + 3 e- → MnO2(s) + 4 OH-(aq) | | |
|
|
|
2.
|
What is the correct cell
notation for a voltaic cell based on the reaction below?
Ni2+(aq) + Zn(s) → Ni(s) + Zn2+(aq)
a. | Zn(s)
Zn2+(aq) 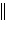 Ni2+(aq) Ni(s) Ni2+(aq) Ni(s) | b. | Zn(s) 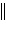 Zn2+(aq), Ni2+(aq)
Ni(s) Zn2+(aq), Ni2+(aq)
Ni(s) | c. | Ni(s) 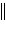 Ni2+(aq), Zn2+(aq)
Ni2+(aq), Zn2+(aq) 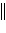 Zn(s)
Zn(s) | d. | Ni(s)
Zn2+(aq) 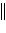 Ni2+(aq) Zn(s) Ni2+(aq) Zn(s) | e. | Ni(s)
Ni2+(aq) 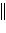 Zn2+(aq) Zn(s) Zn2+(aq) Zn(s) | | |
|
|
|
3.
|
Which of the following species
are likely to behave as oxidizing agents: K+, MnO4-,
Cr2O72-, and I-? a. | K+ only | b. | MnO4- and
Cr2O72- | c. | MnO4-,
Cr2O72-, and I- | d. | Cr2O72- and I- | e. | I- only | | |
|
|
|
4.
|
Consider the following
half-reactions:
Cu2+(aq) + 2 e- → Cu(s)
E° = +0.34 V
Sn2+(aq) + 2 e-
→ Sn(s) E° =
-0.14 V
Fe2+(aq) + 2 e- →
Fe(s) E° = -0.44 V
Al3+(aq) + 3 e-
→ Al(s) E° =
-1.66 V
Mg2+(aq) + 2 e- → Mg(s)
E° = -2.37 V
Which of the above metals or metal ions
will reduce Fe2+(aq)? a. | Cu(s) and Sn(s) | b. | Cu2+(aq) and Sn2+(aq) | c. | Al3+(aq) and Mg2+(aq) | d. | Al(s) and Mg(s) | e. | Sn(s) and
Al3+(aq) | | |
|
|
|
5.
|
Calculate 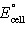 for the electrochemical cell below,
for the electrochemical cell below,
Ag(s)
AgCl(s) Cl-(aq, 1.0 M) 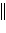 Fe3+(aq, 1.0 M), Fe2+(aq, 1.0 M)
Pt(s)
Fe3+(aq, 1.0 M), Fe2+(aq, 1.0 M)
Pt(s)
given the following reduction half-reactions.
Ag+(aq) + e-
→ Ag(s) E° =
+0.799 V
Fe3+(aq) + e- →
Fe2+(aq) E° = +0.771 V
AgCl(s) + e- → Ag(s) + Cl-(aq) E° =
+0.222 V a. | -0.250 V | b. | -0.028 V | c. | +0.549 V | d. | +0.993 V | e. | +1.570 V | | |
|
|
|
6.
|
A Faraday, F, is defined
as a. | the charge on a single electron. | b. | the charge, in coulombs, carried by one mole of electrons. | c. | the voltage required to reduce one mole of reactant. | d. | the current required to reduce one mole of reactant. | e. | the charge passed by one ampere of current in one second. | | |
|
|
|
7.
|
What is the pH of the solution
at the cathode if 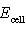 = -0.174 V for the following electrochemical cell at 25
°C? = -0.174 V for the following electrochemical cell at 25
°C?
Pt
H2(g, 1.0 atm) H+(aq, 1.00 M) 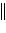 H+(aq) H2(g, 1.0 atm) Pt
H+(aq) H2(g, 1.0 atm) Pt
a. | 2.94 | b. | 5.90 | c. | 6.77 | d. | 8.12 | e. | 13.54 | | |
|
|
|
8.
|
If ΔG° for the following reaction is -324 kJ,
calculate 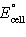 . .
Cr2O72-(aq) + 2 Fe(s) + 14
H+(aq) → 2 Cr3+(aq) + 2
Fe3+(aq) + 7 H2O(l)
a. | -3.36 V | b. | -1.12 V | c. | +0.0201 V | d. | +0.560 V | e. | +1.68 V | | |
|
|
|
9.
|
What charge, in coulombs, is
required to deposit 0.301 g Cu(s) from a solution of Cu2+(aq)? a. | 9.82 × 10-8
C | b. | 3.97 ×
10-4 C | c. | 228 C | d. | 457 C | e. | 914 C | | |
|
|
|
10.
|
Al3+ is reduced to
Al(s) at an electrode. If a current of 2.00 ampere is passed for 48 hours, what mass of aluminum is
deposited at the electrode? Assume 100% current efficiency. a. | 3.58 g | b. | 32.2 g | c. | 48.3 g | d. | 96.6 g | e. | 2.90 × 102
g | | |
|