Multiple
Choice
Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the
question.
|
|
|
1.
|
For the following
reaction,
2 SO3(g) 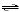 2 SO2(g)
+ O2(g) 2 SO2(g)
+ O2(g)
the equilibrium constant, Kp, is 1.32 at 627 degrees C. What is the
equilibrium constant (Kp) for the reaction below?
SO3(g) 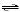 SO2(g) +
1/2 O2(g) SO2(g) +
1/2 O2(g)
a. | 0.660 | b. | 1.15 | c. | 1.32 | d. | 1.74 | e. | 2.64 | |
|
|
|
|
2.
|
The oxidation of sulfur dioxide
produces sulfur trioxide.
2 SO2(g) + O2(g) 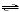 2
SO3(g) 2
SO3(g)
Calculate the value of Kp, given that Kc for the
reaction is 2.3 x
104 at 999 K. (R = 0.08206 L·atm/mol·K)
a. | 3.42 | b. | 2.8 x 102 | c. | 2.9 x
103 | d. | 2.3 x
104 | e. | 1.9 x
106 | |
|
|
|
|
3.
|
When 0.100 mole NH3
is dissolved in water to a volume of 1.00 L, 1.3% of the NH3 reacts with water to form
NH4+. What is the equilibrium constant for the
reaction?
NH3(aq) + H2O(l) 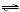 NH4+(aq) +
OH-1(aq) NH4+(aq) +
OH-1(aq)
a. | 5.7 x
10-10 | b. | 1.7 x 10-5 | c. | 1.3 x
10-3 | d. | 1.3 x 10-2 | e. | 7.7 x
102 | |
|
|
|
|
4.
|
Oxygen and ozone form an
equilibrium mixture according to the chemical equation below.
3 O2(g)  2 O3(g) 2 O3(g)
The partial pressure of O2 is measured in a flask at equilibrium as 1.15
atm and the total pressure in the flask is 1.59 atm. Calculate Kp.
a. | 0.13 | b. | 0.38 | c. | 1.66 | d. | 2.6 | e. | 7.7 | |
|
|
|
|
5.
|
Carbonyl bromide decomposes to
carbon monoxide and bromine.
COBr2(g)  CO(g) +
Br2(g) CO(g) +
Br2(g)
Kc is 0.190 at 73 K. If an initial concentration of 0.330 M
COBr2 is allowed to equilibrate, what are the equilibrium concentrations of
COBr2, CO, and Br2?
a. | [COBr2] = 0.230 M, [CO] = 0.100
M, [Br2] = 0.100 M | b. | [COBr2] = 0.138 M, [CO] = 0.162
M, [Br2] = 0.162 M | c. | [COBr2] = 0.157 M, [CO] = 0.173
M, [Br2] = 0.173 M | d. | [COBr2] = 0.209 M, [CO] = 0.121
M, [Br2] = 0.121 M | e. | [COBr2] = 0.157 M, [CO] = 0.081
M, [Br2] = 0.081 M | |
|
|
|
|
6.
|
A 2.00 L flask is filled with
2.5 mol SO3, 2.0 mol SO2, and 0.40 mol O2, and allowed to reach
equilibrium. Predict the effect on the concentrations of SO3 as equilibrium is achieved by
using Q, the reaction quotient. Assume the temperature of mixture is chosen so that
Kc = 1.0.
2 SO3(g)  2 SO2(g)
+ O2(g) 2 SO2(g)
+ O2(g)
a. | [SO3] will decrease because
Q < K. | b. | [SO3] will decrease because
Q > K. | c. | [SO3] will increase because
Q < K. | d. | [SO3] will increase because
Q > K. | e. | [SO3] will remain the same
because Q = K. | |
|
|
|
|
7.
|
Assume that the following
endothermic chemical reaction is at equilibrium.
C(s) + H2O(g)  H2(g) + CO(g) H2(g) + CO(g)
All of the following will increase the ratio of products to reactants
in the equilibrium mixture EXCEPT
a. | increasing the
temperature. | b. | increasing the volume. | c. | decreasing the pressure | d. | addition of solid
carbon. | e. | removal of a gaseous product. | |
|
|
|
|
8.
|
A flask contains the following
chemical system in equilibrium.
Cu(OH)2(s) 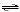 Cu2+(aq)
+ 2 OH-(aq) Cu2+(aq)
+ 2 OH-(aq)
Addition of which of the following reagents would increase the solubility of
Cu(OH)2?
a. | HCl | b. | NaCl | c. | NaOH | d. | Cu(OH)2 | e. | Cu(NO3)2 | |
|
|
|
|
9.
|
Which of the following weak
acids has the strongest conjugate base?
a. | acetic acid, Ka = 1.8
x 10-5 | b. | benzoic acid, Ka = 6.3 x 10-5 | c. | dihydrogen phosphate ion,
Ka = 6.2 x
10-8 | d. | formic acid, Ka = 1.8
x 10-4 | e. | hydrocyanic acid, Ka = 4.0 x 10-10 | |
|
|
|
|
10.
|
Given the following equilibrium
constants,
Ka (HNO2) = 4.5 x 10-4
Kb (NH3) = 1.8 x
10-5
Kw = 1.00 x
10-14
determine the equilibrium constant for the reaction below.
HNO2(aq) + NH3(aq)
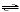 NO2-(aq) +
NH4+(aq) NO2-(aq) +
NH4+(aq)
a. | 2.5 x
10-13 | b. | 8.1 x 10-9 | c. | 8.1 x
105 | d. | 4.0 x
1012 | e. | 2.5 x 1015 | |
|
|
|
|
11.
|
Benzoic acid has a
pKa value of 4.20. What is the value of Kb for sodium
benzoate?
a. | 1.0 x
10-14 | b. | 2.4 x
10-14 | c. | 1.6 x
10-10 | d. | 6.3 x 10-5 | e. | 2.8 x
10-3 | |
|
|
|
|
12.
|
The pH of 0.010 M
trimethylamine is 10.88. What is the value of Kb for this base?
a. | 1.3 x
10-11 | b. | 9.8 x 10-8 | c. | 4.8 x
10-7 | d. | 5.8 x 10-5 | e. | 7.6 x
10-4 | |
|
|
|
|
13.
|
Which of the following chemical
reactions corresponds to Kb2 for Na2SO3?
a. | HSO3-(aq) + H2O(l) 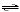 H2SO3(aq) + OH-(aq)
H2SO3(aq) + OH-(aq) | b. | SO32-(aq) + H3O+(aq) 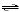 HSO3-(aq) + H2O(l) HSO3-(aq) + H2O(l) | c. | H2SO3(aq) + OH-(aq) 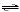 HSO3-(aq) + H2O(l)
HSO3-(aq) + H2O(l) | d. | HSO3-(aq) +
OH-(aq) 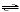 SO32-(aq) +
H2O(l) SO32-(aq) +
H2O(l) | e. | HSO3-(aq) +
H3O+(aq) 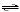 H2SO3(aq) + H2O(l)
H2SO3(aq) + H2O(l) | |
|
|
|
|
14.
|
What is the pH of the solution
which results from mixing 25 mL of 0.20 M CH3CO2H and 25 mL of 0.20 M NaOH?
(Ka for CH3CO2H = 1.8 x 10-5)
a. | 5.13 | b. | 7.00 | c. | 8.87 | d. | 9.02 | e. | 10.43 | |
|
|
|
|
15.
|
What is the pH of a mixture
containing 0.30 M HNO2 and 0.15 M NaNO2? (Ka for
HNO2 = 4.5 x
10-4)
a. | 3.05 | b. | 4.05 | c. | 4.35 | d. | 4.65 | e. | 5.01 | |
|
|
|
|
16.
|
What is the pH of the solution
that results from adding 25 mL of 0.33 M HCl to 25 mL of 0.58 M NH3? (Kb
for NH3 = 1.8 x
10-5)
a. | 3.87 | b. | 4.62 | c. | 8.99 | d. | 9.13 | e. | 9.38 | |
|
|
|
|
17.
|
Which of the following
combinations would be the best to buffer the pH to 7.0?
a. | H3PO4 and H2PO4-,
Ka = 7.5 x
10-3 | b. | HNO2 and
NO2-, Ka = 4.5 x 10-4 | c. | CH3CO2H
and CH3COO-, Ka = 1.8 x 10-5 | d. | H2PO4-
and HPO42-, Ka = 6.2 x 10-8 | e. | NH4+ and NH3, Ka = 5.7 x
10-10 | |
|
|
|
|
18.
|
All of the following will
produce a buffer solution EXCEPT
a. | NH4Cl and
NH3. | b. | HCN and KCN. | c. | NaHCO3 and Na2CO3. | d. | NaH2PO4 and
Na2HPO4. | e. | NaOH and NaCl. | |
|
|
|
|
19.
|
What is the pH of the buffer
that results when 18.0 g of NaCH3CO2 is mixed with 125 mL of 1.00 M
CH3CO2H and diluted with water to 1.00 L? (Ka for
CH3CO2H = 1.8 x
10-5)
a. | 2.44 | b. | 3.87 | c. | 4.14 | d. | 4.74 | e. | 4.99 | |
|
|
|
|
20.
|
What is the pH of a buffer that
results when 25 g NaHCO3 is mixed with 100.0 mL of 2.00 M NaOH and diluted with water to
225 mL? (Ka for HCO3- = 4.8 x 10-11)
a. | 7.88 | b. | 9.36 | c. | 10.05 | d. | 10.27 | e. | 10.63 | |
|
|
|
|
21.
|
If the ratio of base to acid in
a buffer changes by a factor of 10, the pH of the buffer
a. | increases by 2. | b. | increases by 1. | c. | decreases by 1. | d. | decreases by 2. | e. | remains unchanged. | |
|
|
|
|
22.
|
What volume of 0.500 M NaOH
should be added to 750.0 mL of 0.250 M HCO3- to make a buffer with a pH of
10.00? (pKa for HCO3- = 10.32)
a. | 60.7 mL | b. | 82.1 mL | c. | 121 mL | d. | 375 mL | e. | 455 mL | |
|
|
|
|
23.
|
Hydrochloric acid (0.0200 M) is
used to titrate 50.0 mL of 0.0100 M NH3. What is the pH at the equivalence point?
(Kb for NH3 = 1.8 x 10-5)
a. | 1.92 | b. | 3.44 | c. | 4.79 | d. | 5.72 | e. | 8.81 | |
|
|
|
|
24.
|
A 25.0 mL sample of vinegar is
titrated with 0.0950 M NaOH. If the titration requires 35.8 mL of NaOH, what is the concentration of
acetic acid in the vinegar?
a. | 0.0663 M | b. | 0.0971 M | c. | 0.136 M | d. | 0.329 M | e. | 0.727 M | |
|
|
|
|
25.
|
An impure sample of sodium
carbonate, Na2CO3, is titrated with 0.100 M HCl according to the reaction
below.
2 HCl(aq) + Na2CO3(aq) 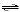 CO2(g) + H2O(l) + 2
NaCl(aq)
CO2(g) + H2O(l) + 2
NaCl(aq)
What is the percent of Na2CO3 in a 0.500 g sample if the
titration requires 37.3 mL of HCl? The molar mass of Na2CO3 is 106.0
g/mol.
a. | 0.746% | b. | 12.7% | c. | 24.5% | d. | 39.5% | e. | 74.6% | |
|
|
Essay - note that these questions will not be graded by the computer, but
answers will be provided
|
|
|
26.
|
The standard enthalpy of
formation of ammonia is -46.1 kJ/mol.
1/2 N2(g) + 3/2 H2(g) 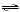 NH3(g) NH3(g)
Commercially, the reaction is carried out at high temperatures. Using your knowledge
of kinetics and equilibrium, explain an advantage and a disadvantage of synthesizing ammonia at high
temperatures.
|
|
|
27.
|
Which
is the stronger Bronsted acid, Fe(H2O)62+ or
Fe(H2O)63+?
Explain.
|
|
|
28.
|
Hyperventilation can cause your
blood pH to rise. One way to lower your blood pH is to breath into a paper bag, thus recycling the
air you exhale. Why does this procedure lower your blood pH?
|
|
|
29.
|
Why do salts containing basic
anions have a greater solubility in water than predicted from calculations using
Ksp values? Examples of such salts are CaCO3, PbF2,
Ca3(PO4)2.
|