Multiple
Choice
Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the
question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Calculate the standard entropy
change for the following reaction,
2 Ag2O(s) → 4
Ag(s) + O2(g)
given Sº[Ag2O] = 121.3 J/K·mol, Sº[Ag(s)] =
42.6 J/K·mol, and Sº[O2(g)] = 205.1 J/K·mol. a. | -205.1 J/K | b. | -126.4 J/K | c. | +126.4 J/K | d. | +132.9 J/K | e. | +205.1 J/K | | |
|
|
|
2.
|
Use the following thermodynamic
data
Species | ΔH
(kJ/mol) | Sº (J/Kmol) | H2O2(l) | -187.78 | 109.6 | H2O(l) | -285.83 | 69.91 | O2(g) | 0 | 205.14 | | | |
to calculate for ΔS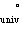 the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide at
25.00 ºC. the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide at
25.00 ºC.
2 H2O2(l) → 2 H2O(l) + O2(g) a. | -657.94 J/K | b. | -532.35 J/K | c. | +125.75 J/K | d. | +435.85 J/K | e. | +783.75 J/K | | |
|
|
|
3.
|
If a process is endothermic and
spontaneous, which of the following must be true? a. | ΔG > 0 and ΔH < 0 | b. | ΔG < 0 and ΔH < 0 | c. | ΔG < 0 and ΔS > 0 | d. | ΔH < 0 and ΔS > 0 | e. | ΔH > 0 and ΔS < 0 | | |
|
|
|
4.
|
Calculate 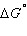 for the reaction below at 25.0ºC. for the reaction below at 25.0ºC.
PCl3(g) + Cl2(g)
→ PCl5(g)
Species | ΔH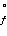 (kJ/mol) (kJ/mol) | ΔS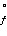 (J/K·mol) (J/K·mol) | PCl3(g) | -287.0 | 311.8 | Cl2(g) | 0 | 223.1 | PCl5(g) | -374.9 | 364.5 | | | |
a. | -1432.6 kJ | b. | -930.1 kJ | c. | -879.0 kJ | d. | -50.8 kJ | e. | -37.1 kJ | | |
|
|
|
5.
|
If ΔGº< 0, then a. | K >1 | b. | K = 0 | c. | K < 1 | d. | K = 1 | e. | K < 0 | | |
|
|
|
6.
|
What is the equilibrium
constant for formation of carbon dioxide at 25ºC? (R = 8.3145
J/K·mol)
C(s) + O2(g) 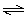 CO2(g) ΔG CO2(g) ΔG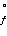 = -3.90 ×
102 kJ/mol = -3.90 ×
102 kJ/mol
a. | 5.7 ×
101 | b. | 5.4 ×
1013 | c. | 2.9 ×
1024 | d. | 4.9 ×
1042 | e. | 2.3 ×
1068 | | |
|
|
|
7.
|
Calculate ΔGº for the following reaction at 298 K,
N2O4(g) 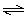 2 NO2(g) 2 NO2(g)
given K = 0.15. (R = 8.3145 J/K •
mol) a. | +1.15 kJ | b. | +4.70 kJ | c. | +8.13 kJ | d. | +38.1 kJ | e. | +87.0 kJ | | |
|
|
|
8.
|
Calculate ΔGfº for CaCO3
given the following information.
C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) | ΔGº = -394.4 kJ | CaO(s) + CO2(g) → CaCO3(s) | ΔGº = -130.4 kJ | Ca(s) + 1/2 O2(g) → CaO(s) | ΔGº = -604.0 kJ | | |
a. | -1128.8 kJ | b. | -340.0 kJ | c. | -130.4 kJ | d. | +868.0 kJ | e. | +1128.8 kJ | | |
|
|
|
9.
|
In the following
reaction,
Fe2+(aq) + Ag+(aq) →
Fe3+(aq) + Ag(s) a. | Fe2+ is oxidized and
Fe3+ is reduced. | b. | Fe2+ is oxidized and
Ag+ is reduced. | c. | Ag+ is oxidized and Ag(s) is
reduced. | d. | Ag+ is oxidized and Fe2+ is
reduced. | e. | Ag+ is oxidized and Fe3+ is
reduced. | | |
|
|
|
10.
|
The fuel cells used aboard
NASA's Space Shuttle are electrochemical cells that generate electricity from which overall chemical
reaction? a. | 2 H2(g) + O2(g) → 2 H2O(l) | b. | NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) | c. | KOH(aq) + AgNO3(aq)
→ AgOH(s) +
KNO3(aq) | d. | CH4(g) + 2 O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2 H2O(g) | e. | HgO(s) + ZnS(s) → HgS(s) +
ZnO(s) | | |
|
|
|
11.
|
Calculate E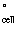 for the following electrochemical cell: for the following electrochemical cell:
Pt | Fe3+(aq),
Fe2+(aq) || Zn2+(aq) | Zn
given the following reduction
half-reactions.
Fe3+(aq) + e-
→ Fe2+(aq) | Eº = +0.771
V | Zn2+(aq) + 2 e- → Zn(s) | Eº = -0.763 V | | |
a. | -1.534 V | b. | -0.008 V | c. | +0.008 V | d. | +1.802 V | e. | +2.305 V | | |
|
|
|
12.
|
Calculate E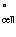 for the following electrochemical cell: for the following electrochemical cell:
Pt | H2(g) | H+(aq)
|| Pb2+(aq) | PbSO4(s) | Pb
given the following standard reduction
potentials.
2 H+(aq) + 2 e-
→ H2(g) | Eº = 0.000
V | PbSO4(s) + 2 e- → Pb(s) + SO 42-(aq) | Eº
= -0.356 V | | |
a. | -0.712 V | b. | -0.356 V | c. | -0.178 V | d. | +0.356 V | e. | +0.712 V | | |
|
|
|
13.
|
Calculate E for the
following electrochemical cell at 25ºC
Ag | Ag+(aq, 0.150 M) || Sn2+(aq, 0.500 M),
Sn4+(aq, 0.500 M) | Pt
given the following standard reduction
potentials.
Ag+(aq) + e-
→ Ag(s) | Eº = +0.80
V | Sn4+(aq) + 2 e- → Sn2+(aq) | Eº = +0.14
V | | |
a. | -0.915 V | b. | -0.61 V | c. | +0.89 V | d. | +0.915 V | e. | +0.99 V | | |
|
|
|
14.
|
If 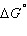 for
the following reaction is -1.73 × 103 kJ,
calculate for
the following reaction is -1.73 × 103 kJ,
calculate 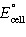 . .
Cr2O72-(aq) + 2 Al(s) + 14 H+(aq)
→ 2 Cr3+(aq) + 2 Al3+(aq) + 7
H2O(l) a. | +1.49 V | b. | +2.18 V | c. | +2.99 V | d. | +4.48 V | e. | +5.98 V | | |
|
|
|
15.
|
Which of the following
equations is the solubility product for Ca(IO3)2? a. | Ksp =
[Ca2+][I-]2[O2-]6 | b. | Ksp =
[Ca2+][I-]2[3O2-]2 | c. | Ksp = [Ca2+][IO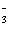 ] ] | d. | Ksp = [Ca2+][IO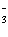 ]2 ]2 | e. | Ksp =
[Ca2+]2[IO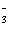 ] ] | | |
|
|
|
16.
|
The solubility of
BaSO4 is 1.05 × 10-5 mol/L. What is the value
of Ksp for BaSO4? a. | 3.24 ×
10-3 | b. | 6.48 ×
10-3 | c. | 2.10 ×
10-5 | d. | 1.10 ×
10-10 | e. | 2.20 ×
10-10 | | |
|
|
|
17.
|
What is the molar solubility of
Ag2CrO4 in 0.20 M K2CrO4? The value of
Ksp for Ag2CrO4 is 9.0 ×
10-12. a. | 4.5 ×
10-11 mol/L | b. | 1.3 ×
10-10 mol/L | c. | 3.6 ×
10-8 mol/L | d. | 3.4 ×
10-6 mol/L | e. | 1.3 ×
10-4 mol/L | | |
|
|
|
18.
|
At what pH will a solution
0.150 M Cu2+ begin to precipitate as Cu(OH)2? The Ksp for
Cu(OH)2 is 1.6 × 10-19. a. | 1.80 | b. | 5.01 | c. | 7.23 | d. | 8.99 | e. | 13.18 | | |
|
|
|
19.
|
A solution contains 0.10 M
Cl- and 0.10 M Br-. If Ag+ is added until AgCl just begins to
precipitate, what are the concentrations of Ag+ and Br-? (Ksp
for AgCl = 1.8 × 10-10, Ksp
for AgBr = 3.3 × 10-13) a. | [Ag+] = 1.8 ×
10-9 M, [Br-] = 3.3 ×
10-12 M | b. | [Ag+] = 1.8 × 10-9 M, [Br-] = 1.8 ×
10-4 M | c. | [Ag+] = 3.3 × 10-12 M, [Br-] = 1.0 ×
10-1 M | d. | [Ag+] = 3.3 × 10-12 M, [Br-] = 1.8 ×
10-4 M | e. | [Ag+] = 1.8. × 10-9 M, [Br-] = 1.8 ×
10-3 M | | |
|
|
|
20.
|
Consider the
reaction
Ni(OH)2(s) + 4 CN-(aq) 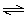 Ni(CN)42-(aq) + 2
OH-(aq) K = 2.8 × 1014
Ni(CN)42-(aq) + 2
OH-(aq) K = 2.8 × 1014
If Ksp for Ni(OH)2 is 2.8 × 10-16, what is the value of the formation constant,
Kform, for the reaction below?
Ni2+(aq) + 4 CN-(aq)
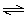 Ni(CN)42-(aq) Ni(CN)42-(aq) a. | 1.0 ×
10-30 | b. | 7.8 ×
10-2 | c. | 1.3 ×
101 | d. | 2.8 ×
102 | e. | 1.0 ×
1030 | | |
|
|
|
21.
|
Only 1.06 g of
Ca(NO3)2 will dissolve per liter of a solution that is buffered to a pH of
13.00. What is the value of Ksp for Ca(OH)2? The molar mass of
Ca(NO3)2 is 164.1 g/mol. a. | 1.8 ×
10-10 M | b. | 4.2 ×
10-7 M | c. | 1.1 ×
10-6 M | d. | 4.2 ×
10-5 M | e. | 6.5 ×
10-5 M | | |
|
|
|
22.
|
Write a balanced half-reaction
for the reduction of NO3-(aq) to NO(g) in an acidic solution. a. | NO3-(aq) + H+(aq) + e- → NO(g) + HO2(aq) | b. | NO3-(aq) + 2
H+(aq) + e- → NO(g)
+ 2 OH-(aq) | c. | NO3-(aq) + 3
e- → NO(g) + 2
O2(g) | d. | NO3-(aq) + 4
H+(aq) + 3 e- → NO(g)
+ 2 H2O(l) | e. | 2 HNO3(aq) + 6 e-
→ NO(g) + H2(g) + 3
O2(g) | | |
|
|
|
23.
|
Write a balanced chemical
equation for the following reaction in a basic solution.
H2O2(aq) +
Cr(OH)3(s) → H2O(l) +
CrO42-(aq) a. | 2 H2O2(aq) + 3
Cr(OH)3(s) → H2O(l) + 3 CrO42-(aq) +
11/2 H+(aq) | b. | 2 H2O2(aq) +
Cr(OH)3(s) → H2O(l) + CrO42-(aq) + 2
OH-(aq) | c. | H2O2(aq)
+ 2 Cr(OH)3(s) → 2 CrO42-(aq)
+ 5 H2O(l) | d. | 3 H2O2(aq) + 2
Cr(OH)3(s) + 4 OH-(aq) → 2
CrO42-(aq) + 8 H2O(l) | e. | 4 H2O2(aq) + 2
Cr(OH)3(s) → 2 H2O(l) + 2 CrO42-(aq) + 4
OH-(aq) | | |
|
|
|
24.
|
Use the standard reduction
potentials below to determine which compound or ion is the best reducing
agent?
Hg2+(aq) + 2 e-
→ Hg(l) | Eº = +0.855 V | Cu2+(aq) + 2 e- →
Cu(s) | Eº = +0.337 V | Cd2+(aq) + 2 e- →
Cd(s) | Eº = -0.40 V | | |
a. | Hg2+ | b. | Hg(l) | c. | Cu2+ | d. | Cd2+ | e. | Cd | | |
|
|
|
25.
|
At what temperature would you
expect a reaction to become spontaneous if ΔH = +67.0 kJ and ΔS = -131 J/K? a. | T < -511
K | b. | T > 238 K | c. | T > 511 K | d. | The reaction will be spontaneous at any
temperature. | e. | The reaction will NOT be spontaneous at any
temperature. | | |
|
Completion
Complete each sentence or statement.
|
|
|
1.
|
The total energy of the
universe is constant. This is a statement of the ________ law of thermodynamics.
|
|
|
2.
|
A chemical reaction with an
equilibrium constant greater than one is said to be ________-favored.
|
|
|
3.
|
For any process, the change in
entropy of the universe equals the sum of the entropy changes to the system and the
________.
|
|
|
4.
|
When a secondary battery
provides electrical energy, it is acting as a voltaic cell. When the battery is recharging, it is
operating as a(n) ________ cell.
|
Essay
|
|
|
1.
|
Does the formation of complex
molecules such as proteins and nucleic acids from more simple molecules break the second law of
thermodynamics?
|
|
|
2.
|
At the boiling point, liquid
and gas phases exist at equilibrium. In addition, for a system at equilibrium ΔGº = 0. Calculate the enthalpy of vaporization of water at its normal
boiling point if ΔSº
[H2O(l)] =
69.9 J/K • mol and ΔSº [H2O(g)] =
188.8 J/K • mol.
|
|
|
3.
|
Explain the function of a salt
bridge in a voltaic cell.
|
|
|
4.
|
Why do salts containing basic
anions have a greater solubility in water than predicted from calculations using
Ksp values? Examples of such salts are CaCO3, PbF2,
Ca3(PO4)2.
|