Multiple
Choice
Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the
question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Which relationship is correct
for the rate of decomposition of dinitrogen pentaoxide?
2 N2O5(g)
→ 4 NO2(g) + O2(g)
|
|
|
2.
|
For the reaction A + 2B
→ C, the rate law is
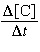 =
k[A][B]2. =
k[A][B]2.
What are the units of the rate constant where time is measured in
seconds?
|
|
|
3.
|
For a second-order
decomposition reaction,
2A → B rate =
k[A]2
which of the following functions can be plotted versus time to give a straight
line? a. | [A] | b. | [A]2 | c. | ln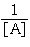 | d. | ln[A] | e. | | | |
|
|
|
4.
|
The reaction A → B follows first-order kinetics with a half-life of 21.7 seconds. If the concentration
of A is 0.430 M after 14.5 seconds, what is the initial concentration of A? a. | 0271 M | b. | 0.287 M | c. | 0.644 M | d. | 0.683 M | e. | 1.59 M | | |
|
|
|
5.
|
Hydrogen peroxide decomposes
into water and oxygen in a first-order process.
H2O2(aq)
→ H2O(l) + 1/2
O2(g)
At 20.0 °C, the half-life for the reaction is 3.92 × 104 seconds. If the initial concentration of hydrogen peroxide is 0.88 M,
what is the concentration after 2.20 days? a. | 0.00 M | b. | 0.031 M | c. | 018 M | d. | 0.44 M | e. | 0.88 M | | |
|
|
|
6.
|
The decomposition of phosphine,
PH3, follows first-order kinetics.
4 PH3(g) →
P4(g) + 6 H2(g)
The half-life for the reaction at 550 °C is 81.3 seconds. How long does it take for 89.0% of a phosphine sample to
decompose? a. | 0.0296 s | b. | 123 s | c. | 259 s | d. | 903 s | e. | 732 s | | |
|
|
|
7.
|
For the second-order reaction
below, the concentration of the product, B, after 444 seconds is 0.0730 M. If no B is initially
present, and the initial concentration of A is 0.744 M, what is the rate
constant? (Hint: find the amount of A remaining from the amount of B formed, then use the second order integrated rate law to find k.)
2A → B rate =
k[A]2
a. | 3.3 ×
10-4 M-1s-1 | b. | 7.4 × 10-4
M-1s-1 | c. | 1.2 ×
10-2 M-1s-1 | d. | 1.3 × 10-3
M-1s-1 | e. | 2.8 ×
10-2 M-1s-1 | | |
|
|
|
8.
|
According to collision theory,
which condition(s) must be met in order for molecules to react?
1. | The reacting molecules must collide with each other to
react. | 2. | A catalyst must be in contact with the reacting molecules for a
reaction to occur. | 3. | The reacting molecules must collide with an orientation that can lead
to rearrangement of the atoms. | | |
a. | 1 only | b. | 2 only | c. | 3 only | d. | 1 and 2 | e. | 1 and 3 | | |
|
|
|
9.
|
For a given reaction, the
activation energy is 21.7 kJ/mol. If the reaction rate constant is 6.4 × 10-4 M-1s-1 at 25.0 °C, what is the reaction rate constant at 72.0 °C?
(R = 8.314 J/K·mol) a. | 1.9 ×
10-4 M-1s-1 | b. | 6.4 × 10-4
M-1s-1 | c. | 2.1 ×
10-3 M-1s-1 | d. | 3.6 × 10-3
M-1s-1 | e. | 2.5 ×
1026 M-1s-1 | | |
|
|
|
10.
|
For the overall
reaction
A + 2B → C
which of the following mechanisms is
consistent with the rate equation below?
rate = k[A] [B]2 a. | 2A + B 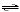 I (fast) I (fast)
I + B → C + A
(slow) | b. | A + B → I
(slow)
I + B
→ C (fast) | c. | 2B → I
(slow)
A + I
→ C (fast) | d. | A + 2B → I
(slow)
I
→ C (fast) | e. | A + 2B → I
(fast)
I + B
→ C + B (slow) | | |
|